|
||
|
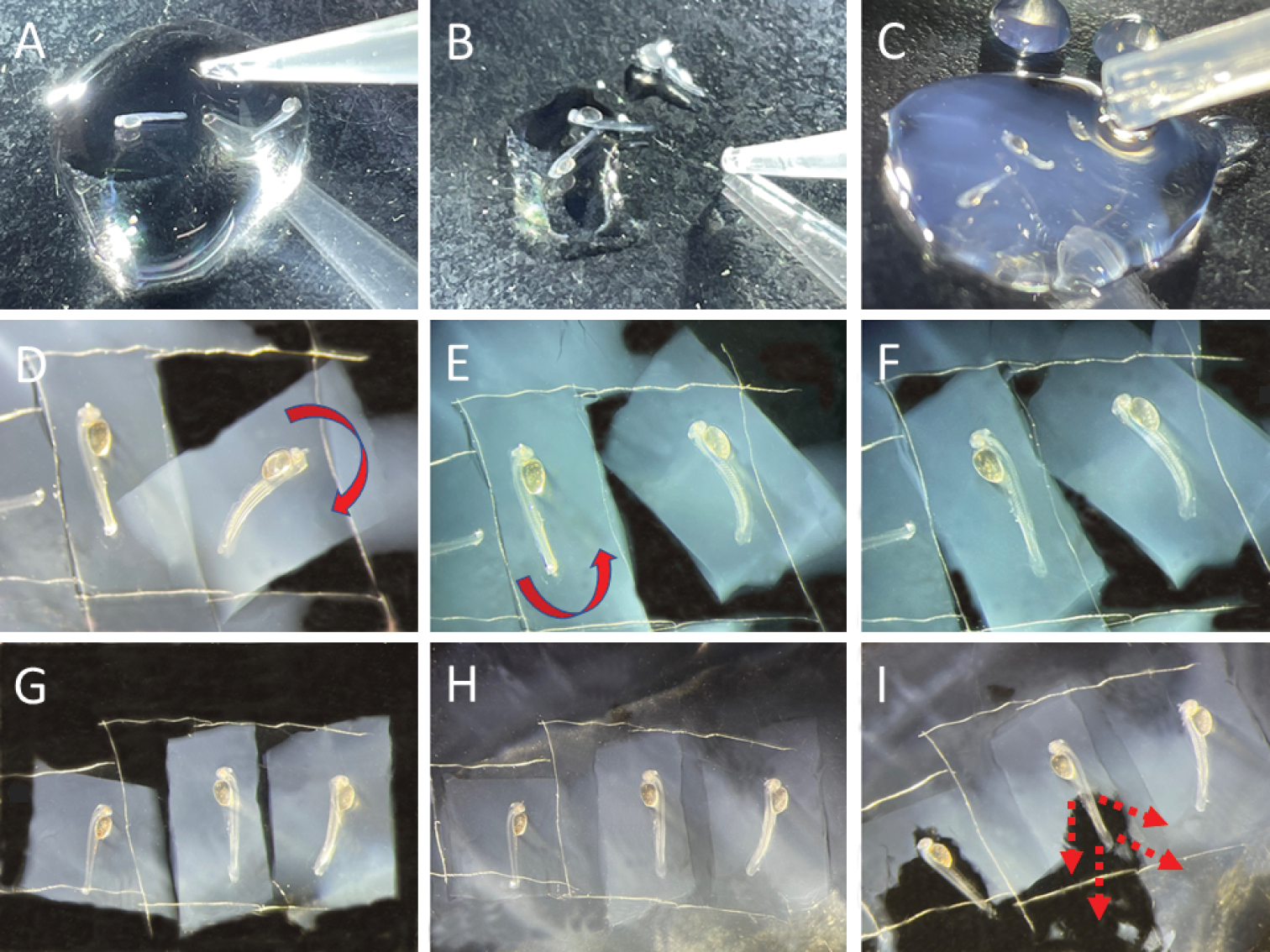
A specimens are transferred to a Petri dish after being in anesthetizing solution for 30 seconds or until embryos stop moving B absorb the excess liquid C add 2% agarose EM. The depth at which the embryo lies should not be too deep because the needle gets deflected from the target, and it is difficult to see the structures. However, it risks detaching the specimen from the agar when barely covered. After agarose solidifies, proceed with lensectomy D–G if lensectomy is to be done on both sides, with a scalpel, cut a rectangle of the agar around the specimen. Very gently slide the scalpel under the rectangle of agar with the specimen. Helped with twicers, flip around the agar slab, so the specimen is on the other side. More than one specimen can be done at a time to increase yield H add 2% agarose around the rectangle of agar or over the specimen if it was dislodged I after the second lensectomy is done, submerge in embryo media and gently dislodge the embryo from the agar with downward strokes starting around the tail and ending on the head. |